Gallstones Flare Up: Understanding Symptoms, Causes, and Management
A gallstones flare up can be an incredibly painful and disruptive experience. Gallstones, small, hard deposits that form in the gallbladder, often cause no symptoms. However, when they block a bile duct, they can trigger a gallstones flare up, characterized by sudden and intense abdominal pain. Understanding what causes these flare-ups, recognizing the symptoms, and knowing how to manage them is crucial for anyone who has been diagnosed with or suspects they might have gallstones. This article provides a comprehensive overview of gallstones flare up, covering everything from the underlying causes to effective treatment strategies.
What are Gallstones?
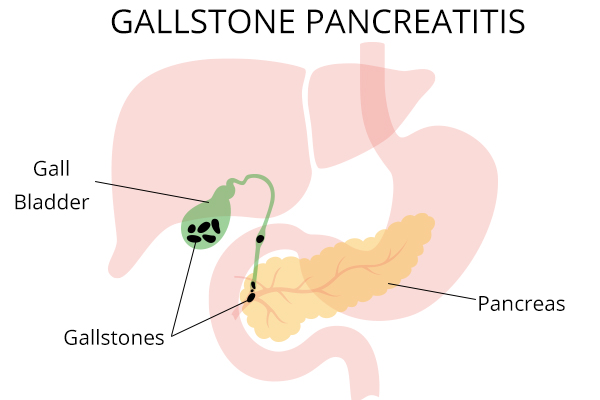
Gallstones are hardened deposits of digestive fluid that can form in your gallbladder, a small organ located beneath the liver. The gallbladder stores bile, a fluid that helps the body digest fats. Gallstones form when there is an imbalance in the components of bile, such as cholesterol, bilirubin, or bile salts. These imbalances can lead to the crystallization of these substances, forming stones that range in size from a grain of sand to a golf ball.
Types of Gallstones
- Cholesterol Stones: These are the most common type of gallstones, typically yellow-green in color. They form when the bile contains too much cholesterol.
- Pigment Stones: These stones are smaller and darker, made of bilirubin. They tend to develop in people with liver disease, blood disorders, or bile duct infections.
- Mixed Stones: As the name suggests, these stones are a mix of both cholesterol and pigment.
Causes of a Gallstones Flare Up
A gallstones flare up occurs when a gallstone blocks one of the bile ducts, usually the cystic duct (leading from the gallbladder) or the common bile duct (leading to the small intestine). This blockage causes pressure to build up in the gallbladder, leading to intense pain. Several factors can trigger a gallstones flare up:
- High-Fat Meals: Fatty foods stimulate the gallbladder to contract and release bile. If a gallstone is present, this contraction can force it into a duct, causing a blockage.
- Rapid Weight Loss: Losing weight too quickly can increase the risk of gallstone formation due to the liver releasing extra cholesterol into the bile.
- Certain Medications: Some medications, such as certain cholesterol-lowering drugs and hormone therapies, can increase the risk of gallstones.
- Underlying Medical Conditions: Conditions like diabetes, Crohn’s disease, and sickle cell anemia can increase the likelihood of developing gallstones.
Symptoms of a Gallstones Flare Up
Recognizing the symptoms of a gallstones flare up is essential for seeking timely medical attention. The primary symptom is a sudden, intense pain in the upper right or center abdomen. This pain, often referred to as a biliary colic, can last from several minutes to several hours. Other common symptoms include:
- Severe Abdominal Pain: This is the hallmark symptom, often described as a sharp, cramping pain.
- Pain Radiating to the Back or Shoulder: The pain can sometimes spread to the back, between the shoulder blades, or to the right shoulder.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Many people experience nausea and vomiting during a gallstones flare up.
- Indigestion and Bloating: These symptoms can occur even after eating small meals.
- Jaundice: In severe cases, where the bile duct is completely blocked, jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes) may occur.
- Fever and Chills: These symptoms can indicate an infection, known as cholecystitis, and require immediate medical attention.
Diagnosing a Gallstones Flare Up
If you suspect you are experiencing a gallstones flare up, it’s crucial to seek medical attention. A doctor will typically perform a physical examination and order several diagnostic tests to confirm the diagnosis. Common diagnostic tests include:
- Abdominal Ultrasound: This is the most common imaging test used to detect gallstones. It is non-invasive and can quickly visualize the gallbladder and bile ducts.
- Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS): This test involves inserting a thin, flexible tube with an ultrasound probe attached into the esophagus. It provides detailed images of the gallbladder and bile ducts.
- HIDA Scan (Hepatobiliary Iminodiacetic Acid Scan): This nuclear medicine scan evaluates the function of the gallbladder and bile ducts.
- CT Scan (Computed Tomography Scan): A CT scan can provide detailed images of the abdomen and can help rule out other causes of abdominal pain.
- Blood Tests: Blood tests can check for signs of infection, inflammation, or liver dysfunction.
Managing a Gallstones Flare Up
The management of a gallstones flare up depends on the severity of the symptoms and the overall health of the individual. Treatment options range from conservative measures to surgical intervention.
Conservative Management
For mild to moderate symptoms, conservative management strategies may be sufficient. These include:
- Pain Management: Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help alleviate mild pain. In more severe cases, prescription pain medications may be necessary.
- Dietary Changes: Avoiding high-fat foods and eating smaller, more frequent meals can help reduce the workload on the gallbladder.
- Hydration: Drinking plenty of fluids can help maintain proper bile flow and prevent further gallstone formation.
Medical Treatment
If conservative measures are not effective, or if the symptoms are severe, medical treatment may be necessary.
- Ursodeoxycholic Acid (UDCA): This medication can help dissolve cholesterol gallstones over time. However, it is not effective for pigment stones and can take several months to years to work.
- ERCP (Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography): This procedure is used to remove gallstones that are lodged in the common bile duct. A thin, flexible tube with a camera and instruments is inserted through the mouth into the small intestine to access the bile duct and remove the stones.
Surgical Treatment
The most common and effective treatment for gallstones is surgical removal of the gallbladder, known as cholecystectomy.
- Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy: This minimally invasive procedure involves making several small incisions in the abdomen and using a camera and specialized instruments to remove the gallbladder. It is associated with less pain, a shorter hospital stay, and a faster recovery compared to open surgery.
- Open Cholecystectomy: This traditional surgical approach involves making a larger incision in the abdomen to remove the gallbladder. It is typically reserved for cases where laparoscopic surgery is not possible or if there are complications.
Preventing Gallstones Flare Ups
While it may not always be possible to prevent gallstones, certain lifestyle modifications can help reduce the risk of a gallstones flare up:
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Avoid rapid weight loss, which can increase the risk of gallstone formation.
- Eat a Balanced Diet: Focus on a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, and limit your intake of high-fat and processed foods.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water to help maintain proper bile flow.
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity can help maintain a healthy weight and reduce the risk of gallstones.
- Consider Medications: If you are at high risk of developing gallstones, talk to your doctor about medications like ursodeoxycholic acid, which can help prevent their formation.
Living with Gallstones
Living with gallstones can be challenging, especially if you experience frequent gallstones flare up. However, with proper management and lifestyle modifications, it is possible to minimize the impact of gallstones on your quality of life. Regular follow-up with your healthcare provider is essential to monitor your condition and adjust your treatment plan as needed.
A gallstones flare up can be a painful and disruptive experience. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and management options is crucial for anyone dealing with this condition. By adopting a healthy lifestyle, seeking timely medical attention, and following your doctor’s recommendations, you can effectively manage your gallstones and prevent future flare-ups. Remember, early diagnosis and treatment are key to minimizing complications and improving your overall well-being. If you suspect you are having a gallstones flare up, do not hesitate to seek medical advice. Understanding the nuances of a gallstones flare up can empower you to take control of your health. Recognizing a gallstones flare up early can lead to quicker intervention and relief. For ongoing health and wellness, it is important to understand how to manage a gallstones flare up. A gallstones flare up can significantly impact daily life, so knowing how to prevent and treat it is vital. The pain from a gallstones flare up is often severe, making prompt medical attention essential. Managing a gallstones flare up effectively involves a combination of lifestyle changes and medical treatments. Preventing a gallstones flare up involves adopting a healthy lifestyle and avoiding triggers. A gallstones flare up can be a recurring issue, so long-term management is important. Seeking professional medical advice is crucial when dealing with a gallstones flare up. The severity of a gallstones flare up can vary, requiring tailored management strategies. Even after treatment, understanding how to prevent a future gallstones flare up is crucial.
[See also: Gallbladder Diet: What to Eat and What to Avoid]
[See also: Cholecystectomy Recovery: A Comprehensive Guide]
[See also: Non-Surgical Gallstone Treatment Options]
