Mastering Efficiency: Lean Manufacturing and Its Synergies with Master Production Scheduling
In today’s competitive global market, manufacturers are constantly seeking ways to optimize their operations, reduce waste, and increase efficiency. Two powerful methodologies, lean manufacturing and Master Production Scheduling (MPS), stand out as crucial tools for achieving these goals. This article delves into the core principles of lean manufacturing, explores its relationship with MPS, and provides practical insights on how to effectively implement these strategies within your organization. Understanding the synergy between lean manufacturing and a robust MPS system is vital for companies looking to enhance productivity, minimize costs, and deliver superior value to their customers.
Understanding Lean Manufacturing
Lean manufacturing, often referred to simply as “lean,” is a systematic approach to minimizing waste within a manufacturing system without sacrificing productivity. It stems from the Toyota Production System (TPS) developed in post-World War II Japan. The core principle of lean manufacturing is to eliminate anything that does not add value from the customer’s perspective. This includes reducing inventory, minimizing defects, shortening lead times, and optimizing workflows.
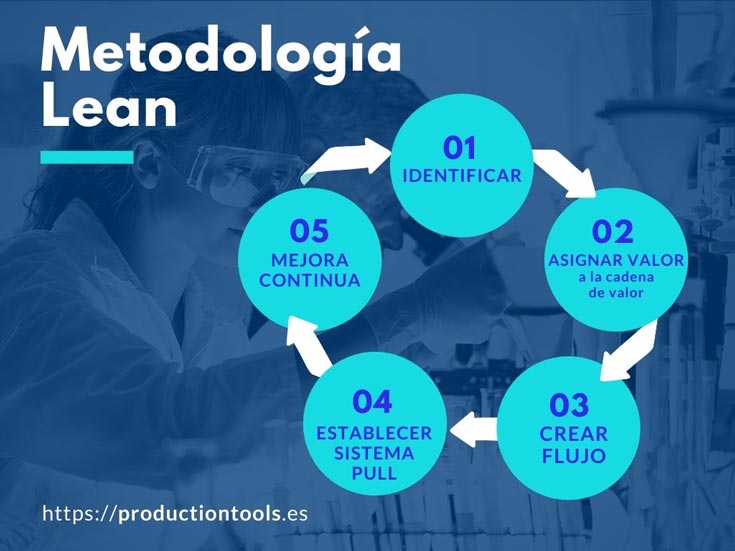
The Five Principles of Lean Manufacturing
- Value: Identify what the customer values. This requires understanding their needs, preferences, and willingness to pay.
- Value Stream: Map out the entire process, from raw materials to finished product, to identify areas of waste.
- Flow: Create a smooth, continuous flow of materials and information throughout the value stream.
- Pull: Implement a “pull” system, where production is triggered by actual customer demand, rather than a “push” system based on forecasts.
- Perfection: Continuously strive for improvement by eliminating waste and optimizing processes.
Key Tools and Techniques in Lean Manufacturing
- 5S Methodology: Sort, Set in Order, Shine, Standardize, and Sustain – a system for organizing and maintaining a clean and efficient workplace.
- Value Stream Mapping (VSM): A visual tool for analyzing the current state of a process and designing a future state with reduced waste.
- Kanban: A visual signaling system that controls the flow of materials and ensures that production is only triggered when needed.
- Kaizen: Continuous improvement through small, incremental changes.
- Just-in-Time (JIT): A production strategy that aims to minimize inventory by producing goods only when they are needed.
- Total Productive Maintenance (TPM): A system for maintaining equipment and preventing breakdowns.
Master Production Scheduling (MPS): A Foundation for Lean
Master Production Scheduling (MPS) is a critical component of production planning. It is a detailed plan that outlines what products need to be produced, how many of each product are required, and when they need to be completed. A well-designed MPS is essential for effective resource allocation, inventory management, and customer order fulfillment. Critically, it provides the framework for the implementation of lean manufacturing principles. Think of MPS as the backbone, and lean manufacturing as the muscle that allows the body to perform efficiently.
The Role of MPS in Supporting Lean Initiatives
While lean manufacturing focuses on eliminating waste and improving efficiency, MPS provides the structure and visibility needed to effectively manage production activities. Here’s how MPS supports lean manufacturing:
- Demand Planning: MPS utilizes demand forecasts and customer orders to create a realistic production plan, preventing overproduction and minimizing excess inventory, both of which are key objectives of lean manufacturing.
- Resource Allocation: MPS helps allocate resources effectively by providing a clear picture of production requirements. This ensures that materials, equipment, and labor are available when needed, preventing bottlenecks and delays.
- Capacity Planning: MPS considers production capacity constraints and identifies potential bottlenecks. This allows manufacturers to proactively address capacity issues and optimize production schedules to meet customer demand.
- Order Promising: MPS enables manufacturers to provide accurate delivery dates to customers by considering production capacity and material availability. This improves customer satisfaction and strengthens customer relationships.
- Stability and Visibility: A stable and visible MPS is critical for implementing lean manufacturing principles. With a clear production plan, manufacturers can focus on improving processes and eliminating waste without constantly reacting to unexpected changes.
Synergies Between Lean Manufacturing and MPS
The true power of lean manufacturing is unlocked when it is integrated with a robust MPS system. When implemented together, these methodologies create a synergistic effect that drives significant improvements in efficiency, productivity, and profitability. Let’s explore some key synergies:
Reduced Inventory Levels
Lean manufacturing aims to minimize inventory by implementing JIT principles and reducing lead times. MPS supports this goal by providing a clear picture of demand and production requirements, allowing manufacturers to optimize inventory levels and reduce carrying costs. By using an accurate MPS, companies can avoid overstocking materials, which is a common source of waste. [See also: Inventory Management Techniques].
Improved Production Flow
Lean manufacturing emphasizes the importance of creating a smooth, continuous flow of materials and information throughout the value stream. MPS supports this by providing a detailed production schedule that minimizes bottlenecks and delays. A well-designed MPS can help manufacturers optimize production sequences, reduce setup times, and improve overall production flow. This improved flow directly contributes to the waste reduction goals of lean manufacturing.
Enhanced Customer Satisfaction
Both lean manufacturing and MPS contribute to enhanced customer satisfaction. Lean manufacturing focuses on delivering value to the customer by reducing lead times and improving product quality. MPS supports this by enabling manufacturers to provide accurate delivery dates and meet customer demand on time. By combining these two methodologies, manufacturers can deliver superior value to their customers and build stronger customer relationships. A satisfied customer is a returning customer, which leads to long-term profitability.
Increased Efficiency and Productivity
The combined effect of lean manufacturing and MPS is a significant increase in efficiency and productivity. Lean manufacturing eliminates waste and optimizes processes, while MPS provides the structure and visibility needed to manage production activities effectively. By integrating these two methodologies, manufacturers can achieve significant improvements in throughput, reduce costs, and increase profitability. This translates to a more competitive and sustainable business.
Implementing Lean Manufacturing with MPS
Implementing lean manufacturing with MPS requires a strategic approach and a commitment to continuous improvement. Here are some key steps to consider:
- Assess Your Current State: Conduct a thorough assessment of your current manufacturing processes to identify areas of waste and inefficiency. This assessment should include a review of your MPS system, inventory levels, production flow, and customer demand patterns.
- Develop a Lean Implementation Plan: Based on your assessment, develop a comprehensive lean manufacturing implementation plan. This plan should outline specific goals, objectives, and timelines. It should also identify the key tools and techniques that will be used to achieve these goals.
- Optimize Your MPS System: Ensure that your MPS system is aligned with your lean manufacturing goals. This may involve updating your demand forecasting methods, improving your resource allocation processes, and optimizing your production schedules.
- Train Your Employees: Provide comprehensive training to your employees on lean manufacturing principles and techniques. This training should cover topics such as 5S, VSM, Kanban, and Kaizen.
- Implement Pilot Projects: Start with small pilot projects to test your lean manufacturing initiatives and refine your implementation plan. This will allow you to identify potential challenges and make adjustments before rolling out the changes across your entire organization.
- Monitor and Measure Results: Continuously monitor and measure the results of your lean manufacturing initiatives. Track key performance indicators (KPIs) such as inventory levels, lead times, production costs, and customer satisfaction. Use this data to identify areas for improvement and make adjustments to your implementation plan as needed.
- Foster a Culture of Continuous Improvement: Create a culture of continuous improvement within your organization. Encourage employees to identify and eliminate waste in their daily activities. Recognize and reward employees who contribute to lean manufacturing initiatives.
Challenges and Considerations
While the benefits of integrating lean manufacturing and MPS are significant, there are also challenges and considerations to keep in mind. Some of these include:
- Resistance to Change: Implementing lean manufacturing and MPS often requires significant changes to existing processes and workflows. This can lead to resistance from employees who are comfortable with the status quo.
- Data Accuracy: Accurate data is essential for effective MPS and lean manufacturing. Inaccurate data can lead to poor production planning, excess inventory, and missed customer deadlines.
- Complexity: Implementing lean manufacturing and MPS can be complex, especially in large organizations with multiple product lines and production facilities.
- IT Infrastructure: A robust IT infrastructure is essential for supporting MPS and lean manufacturing initiatives. This includes having the right software and hardware to manage data, track inventory, and monitor production activities.
- Leadership Commitment: Strong leadership commitment is essential for the success of lean manufacturing and MPS initiatives. Leaders must champion the changes, provide resources, and hold employees accountable for results.
Conclusion
Lean manufacturing and Master Production Scheduling (MPS) are powerful methodologies that can significantly improve efficiency, productivity, and profitability in manufacturing operations. By understanding the core principles of lean manufacturing and integrating it with a robust MPS system, manufacturers can eliminate waste, optimize resource allocation, and deliver superior value to their customers. While implementing these methodologies can be challenging, the benefits are well worth the effort. By following a strategic approach and fostering a culture of continuous improvement, manufacturers can achieve significant and sustainable improvements in their operations. Embracing lean manufacturing principles, supported by a strategic MPS, is not just a trend, but a necessity for survival and success in today’s competitive landscape. The integration of these methodologies ensures a streamlined, efficient, and customer-centric manufacturing environment, allowing companies to thrive in a dynamic market. [See also: The Future of Manufacturing].
